9. Calculation and Report
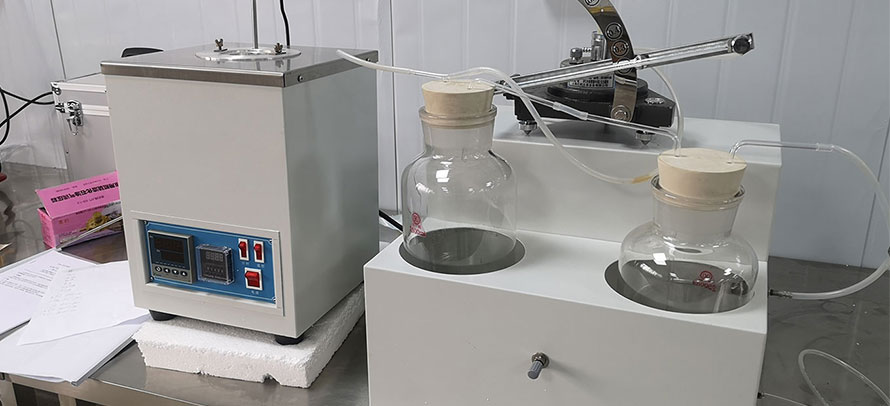
9.1 Calculate and report the oil output from the mist generator after break-in in grams per hour as follows:
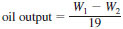
where:
W1 = weight of the mist generator at the start of the test, g, and
W2 = weight of the mist generator after 19 h, g.
9.2 Calculate and report the percent of reclassified oil as follows:
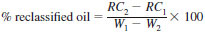
where:
RC1 = weight of the reclassified oil collector at the start of the test, g,
RC2 = weight of the reclassified oil collector at the end of the test, g.
9.3 Calculate and report the percent of line condensate as follows:
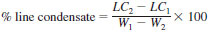
where:
LC1 = weight of the line condensate bottles at the start of the test, and
LC2 = weight of the line condensate bottles at the end of the test.
9.4 Calculate and report the percent of stray mist as follows:
% stray mist = 100 - (% reclassified oil + % line condensate)
NOTE 5 - For design considerations, it may be desirable to calculate the output oil mist density or effective oil mist density, or both. These calculations are made as follows:
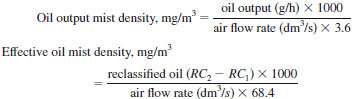
10. Precision and Bias
10.1 The precision of this test method as determined by statistical examination of interlaboratory results is as follows:
10.1.1 Repeatability - The difference between successive results obtained by the same operator with the same apparatus under constant operating conditions on identical test material would, in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed the following values only in one case in twenty:

10.1.2 Reproducibility - The difference between two single and independent results obtained by different operators working in different laboratories on identical test material would, in the long run, exceed the following values only in one case in twenty:

10.2 Bias - The procedure in this test method has no bias because the values of Oil Output, percent Reclassified Oil, and percent Line Condensate can be defined only in terms of a test method.
NOTE 6 - The percent of stray mist is obtained by calculation rather than by a direct determination. Therefore, no precision data are included for percent of stray mist.

