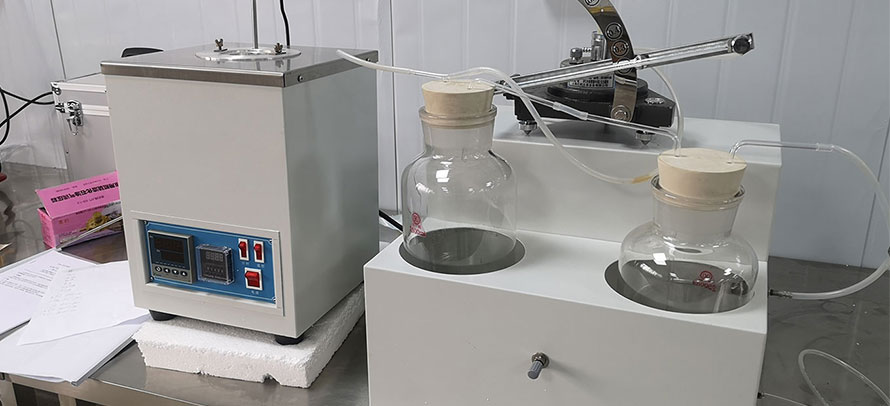
ASTM D4628 standard test method for analysis of barium, calcium, magnesium, and zinc in unused lubricating oils by atomic absorption spectrometry
10. Procedure (Barium)
10.1 Weigh the sample to three significant figures into a 60-mL (2-oz) bottle. The sample mass is chosen to give an absorbance reading of 0.2 to 0.5. Add base oil to make 0.25 more or less 0.01 g total mass. Add 50 mL of potassium suppressant solution, see 6.5, and dissolve. The maximum sample size to be used is 0.25 g, and the minimum is 0.05 g.
10.1.1 To hazy samples add 0.25 more or less 0.01 mL of 2-ethyl hexanoic acid and shake. If this clears up the haze, the analysis is run, and the dilution error is corrected by multiplying the found results by 1.005. If the sample remains hazy, the sample is not suitable to be analyzed by this test method.
10.2 Samples yielding absorbances greater than 0.5 even with the minimum sample size can be accurately diluted with new base oil to a suitable concentration. Make sure the new solution is homogeneous before proceeding as instructed in 10.1.
10.3 Aspirate the sample solution and determine the absorbance, aspirating solvent alone before and after each reading.
11. Calculation (Barium)
11.1 Read from the calibration curve the concentration, C, corresponding to the measured absorbance.
C = concentration of barium in the diluted sample solution, mg/50 mL of suppressant solution.
11.2 Calculate the barium content of the oils in percent mass as follows:
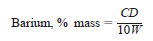
where:
W = grams of sample/50 mL,
C = milligrams of metal/50 mL, and
D = dilution factor if dilution was necessary in 10.2.
NOTE 9 - If the calibration curve is linear, the concentration may be determined by an equation instead of a calibration curve.
12. Calcium Determination
12.1 Repeat Sections 7 through 10 replacing references made to barium with calcium using the following conditions:
12.1.1 Acetylene/nitrous oxide flame,
12.1.2 Calcium hollow cathode lamp, and
12.1.3 Analytical line 422.7 nm.
13. Magnesium Determination
13.1 Repeat Sections 7 through 10 replacing references made to barium with magnesium using the following conditions:
13.1.1 Acetylene/nitrous oxide flame,
13.1.2 Magnesium hollow cathode lamp, and
13.1.3 Analytical line 285.2 nm.
14. Zinc Determination
14.1 Repeat Sections 7 through 10 replacing references made to barium with zinc using the following conditions:
14.1.1 Acetylene/nitrous oxide flame,
14.1.2 Zinc hollow cathode lamp, and
14.1.3 Analytical line 213.9 nm.
NOTE 10 - Although this test method has been described for the determination of four elements on a single sample, the sequence of operations in analyzing several samples should also be considered. Aspiration of a sample to determine its absorbance is very quick. Changing wavelength setting and lamps takes longer. Thus, it is most economical to make measurements at a single wavelength on a series of samples and standards before changing conditions.

