1 Scope
This International standard describes methods for the determination of the dielectric dissipation factor (tan δ), relative permittivity and d.c. resistivity of any insulating liquid material at the test temperature.
The methods are primarily intended for making reference tests on unused liquids. They can also be applied to liquids in service in transformers, cables and other electrical apparatus. However the method is applicable to a single phase liquid only. When it is desired to make routine determinations, simplified procedures, as described in Annex C, may be adopted.
With insulating liquids other than hydrocarbons, alternative cleaning procedures may be required.
2 Normative references
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
IEC 60093, Methods of test for volume resistivity and surface resistivity of solid electrical insulating materials
IEC 60250, Recommended methods for the determination of the permittivity and dielectric dissipation factor of electrical insulating materials at power, audio and radio frequencies including metre wavelengths
IEC 60475, Method of sampling liquid dielectrics
IEC 61620, Insulating liquids - Determination of the dielectric dissipation factor by measurement of the conductance and capacitance - Test method
3 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following terms and definitions apply.
3.1 permittivity (relative)
the relative permittivity of an insulating material is the ratio of capacitance Cx of a capacitor in which the space between and around the electrodes is entirely and exclusively filled with the insulating material in question, to the capacitance Co of the same configuration of electrodes in vacuum.
The capacitance Ca of the configuration of electrodes in air can normally be used instead of Co to determine the relative permittivity with sufficient accuracy
3.2 dielectric dissipation factor (tan δ)
DDF
dielectric dissipation factor, DDF, (tan δ) of an insulating material is the tangent of the loss angle.
The loss angle is the angle by which the phase difference between applied voltage and the resulting current deviates from π/2 rad when the dielectric of the capacitor consists exclusively of the insulating material.
NOTE For practical purposes, measured values below 0.005 for tan δ and power factor are essentially the same. A simple conversion can be used to convert one to the other. The power factor is the sine of the loss angle and the relationship between power factor and dielectric dissipation factor can be expressed as follows:
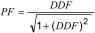
3.3 d.c. resistivity (volume)
the volume resistivity of an insulating material is the quotient of a d.c. electrical field strength and the steady state current density within the material.
NOTE The unit of resistivity is the ohmmetre (Ωm).

