EXPLANATION
This test method covers the determination of the apparent viscosity of hot melt adhesives and coating materials compounded with additives and having apparent viscosities up to 200 000 mPa. s at temperatures up to 175° C. It is believed that apparent viscosity determined by this test method is related to flow performance in application machinery operating under conditions of low shear rate. The results of this test may not correlate well with end use applications where high shear rates are encountered. This test method may be adaptable to viscosities higher than the present 200 000 mPa. s limit and temperatures above 175° C. However, precision of this case has not been studied. This test method is applicable to fluid hot melts having apparent viscosities up to 20 Pa•s at temperatures up to 175° C.
TEST SUMMARY
Approximately 800 g of the sample is melted on a hot plate or in an oven. An 800 mL beaker, which is jacketed with an electric heating mantle, is filled with the melted sample to a level of about 1 in. from the top. The viscometer, with attached spindle and guard, is properly positioned. Stirring is begun and continued while the temperature of the sample is brought to slightly above the highest desired test temperature. Heating is discontinued but stirring is maintained until the sample cools to the chosen temperature. At this point the apparent viscosity is determined. Additional determinations are made as the sample cools. Results of temperature and apparent viscosity are plotted on a semilog paper, and values at any particular temperature are determined from the curve.
TEST PRECISION
See the precision results as follows:
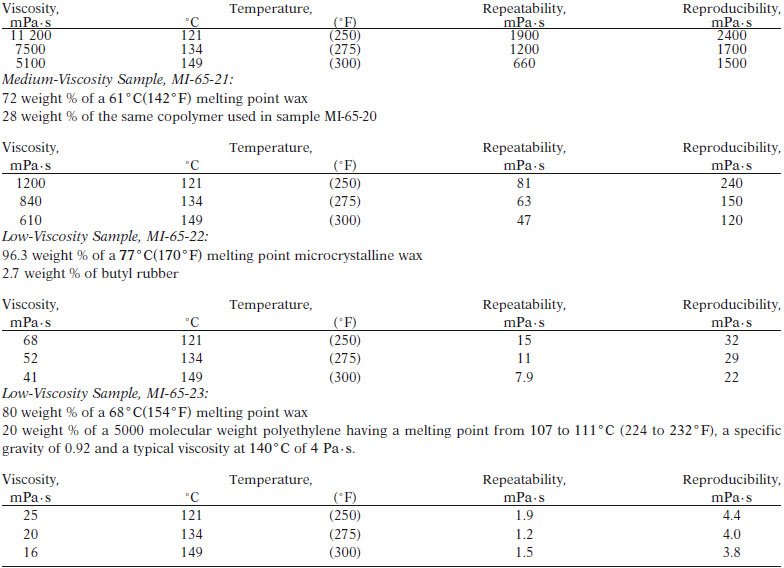
High-Viscosity Sample, MI-65-20:
58 weight % of a 68° C (155° F) melting point wax.
42 weight % of an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer containing 27 to 29 % vinyl acetate and having a melt index of from 12 to 18.

