PROCEDURE B - AUTOMATIC (DIGITAL) PROCEDURE
16. Apparatus
16.1 Refractometer - Automatic digital refractometer with a suitable measuring range of 1.3300 to 1.5000 or higher, capable of displaying the measured refractive index automatically and digitally. The instrument shall incorporate a solvent-resistant prism seal.
16.2 Temperature Control Unit - See 6.2.
16.3 Temperature Measuring Device - A platinum resistance probe or equivalent. The accuracy and resolution of the temperature measuring device shall be 0.1°C or better.
16.4 Light Source - Filtered white light such as that obtained using a tungsten-halogen lamp or a light emitting diode (LED), capable of providing the sodium D spectral line at 589 nm.
16.5 Light Filters - See 6.5.
17. Reagents and Materials
17.1 See Section 7.
18. Sampling
18.1 See Section 8.
19. Preparation of Apparatus
19.1 See Section 9. Ensure that the instrument has a solvent resistant prism seal.
20. Calibration of the Refractometer Using Liquid Reference Standards 20.1 Automatic digital refractometers are normally calibrated using liquid reference standards (see 7.4 and 7.5). They may require a single, two-point, or multi-point calibration. Follow manufacturer's instruction in calibrating the particular automatic digital refractometer being used.
21. Procedure
21.1 Ensure that the prism and the surrounding plate and dish/plate (and presser, if fitted) are thoroughly cleaned as in 9.1. Ensure the prism temperature is correct and the instrument has been properly calibrated.
21.2 Introduce the test sample to the prism ensuring that the prism is adequately covered. Do not introduce an excessive amount because this can slow the thermal equilibration. Lower the sample presser (if fitted).
21.3 Take a succession of readings, noting values, until a steady value is obtained. Record or report, or both, this value as the refractive index of the sample at the test temperature.
NOTE 8 - From experience using the instrument, the user will be able to judge with a safe margin the amount of time needed for a sample to thermally equilibrate on the prism. Based on this, it may be possible on some models to set an automatic delay time for readings. This enables a fixed measuring time to be written in to the experimental protocol.
NOTE 9 - When successive readings are drifting, the direction of drift will indicate what is happening to the sample. An upward drift means the sample is cooling on the prism; a downward drift means the sample is warming up. This is particularly noticeable when samples are much hotter or cooler than the prism.
22. Quality Control
22.1 See Section 13.
23. Report
23.1 An automatic digital electronic refractometer shall provide a direct and digital reading of refractive index. This can be manually recorded or, if the refractometer is equipped with a computer interface, readings can be sent to a printer or to a computer.
23.2 Report the refractive index to four decimal places and the test temperature, for example:
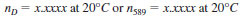
where D or the 589 signifies that the sodium D spectral line was used.
24. Precision and Bias
24.1 Precision - Refractive Index:
24.1.1 The precision for the automatic digital refractive index procedure, as determined by the statistical examination of interlaboratory test results conducted in 1996 on eight different samples from ten laboratories, is as follows:
24.1.2 Repeatability - The difference between successive test results, obtained by the same operator with the same apparatus, under constant operating conditions, and on identical test material, would, in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed the following values only in one case in twenty (95 % confidence level):
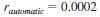
24.1.3 Reproducibility - The difference between two, single and independent results obtained by different operators working in different laboratories on identical test material would, in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed the following values only in one case in twenty (95 % confidence level):
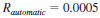
24.1.4 The precision of this test method for automatic refractive index was obtained in accordance with Practice D6300 using the D02 Precision Program (D2PP) software.
24.2 Relative Bias - The 1996 interlaboratory study did not indicate any relative bias between automatic and manual refractive index instruments.
25. Keywords
25.1 refractive dispersion; refractive index; refractometer



