handling point, n - an indication of the minimum temperature to which an oil should be heated in any part of the suction or delivery line of an oil-handling installation when the installation is operating.
handling point, n - an indication of the minimum temperature to which an oil should be heated in any part of the suction or delivery line of an oil-handling installation when the installation is operating. If the storage tank does not contain an outflow heater, this temperature is necessarily the minimum oil storage temperature.
hard carbon, n - see non-graphitizable carbon.
hardness, n - of an elastomer, the resistance to deformation or indentation.
DISCUSSION - In this test method the hardness of an elastomer is measured with a Shore Durometer A (see Test Method D2240).
hardness, n - resistance to permanent deformation or indentation.
hardness, n - the resistance of a material to deformation, particularly permanent deformation, indentation, or scratching.
headspace, n - the unfilled capacity of an ampule that allows for physical expansion due to temperature and pressure changes of the filled material while maintaining the integrity of the package.
heavy distillate, n - a fuel produced from the distillation of crude oil which has a kinematic viscosity at 40°C between 5.5 and 24.0 mm2/s, inclusive.
heavy distillate, n - in the petroleum industry, a distillate whose entire boiling range lies above about 350°C (about 660°F) atmospheric equivalent temperature (AET), and excludes residual bottoms.
DISCUSSION - Heavy distillates are usually obtained from vacuum distillation as the temperatures required for distillation under atmospheric pressures are often high enough to initiate cracking or thermal degradation. For comparison, the temperatures in the vacuum distillation have to be converted to what they would have been under atmospheric conditions as atmospheric equivalent temperatures (AET).
heavy distillate/residual fuel oil blend, n - a blend of heavy distillate and residual fuel oil having a viscosity at 40°C between 5.5 and 24.0 mm2/s, inclusive.
heavy duty, adj - in internal combustion engine operation, characterized by average speeds, power output, and internal temperatures that are close to the potential maximums.
heavy-duty engine, n - in internal combustion engines, one that is designed to allow operation continuously at or close to its peak output.
heavy-duty engine, n - in internal combustion engine types, one that is designed to allow operation continuous at or close to its peak output.
DISCUSSION - This type of engine is typically installed in large trucks and buses as well as farm, industrial, and construction equipment.
heavy scum, n - assessment that the fuel/water interface is covered with more than 50% scum that extends into either of the two layers or forms an emulsion (1 mL or greater in volume), or both.
Henry's Law, n - the principle that the mass of a gas dissolved in a liquid is proportional to the pressure of the gas above the liquid.
Henry's Law, n - the principle that the ratio of partial pressure to mole fraction of gas in solution is a constant.
DISCUSSION - In non-ideal systems the fugacity is used to replace the pressure, but the systems within the scope of this test method can be considered ideal within the limits of the accuracy statement.
Hertzian contact area, n - the apparent area of contact between two nonconforming solid bodies pressed against each other, as calculated from Hertz' equations of elastic deformation.
Hertzian contact area, n - apparent area of contact between two nonconforming solid bodies pressed against each other, as calculated from Hertz's equations of elastic deformation published in 1881.
Hertzian contact pressure, n - the magnitude of the pressure at any specified location in a Hertzian contact area, as calculated from Hertz' equations of elastic deformation.
Hertzian contact pressure, n - magnitude of the pressure at any specified location in a Hertzian contact area, as calculated from Hertz's equations of elastic deformation. The Hertzian contact pressure can also be calculated and reported as maximum value Pmax in the centre of the contact or as Paverage as average over the total contact area.
Hertz line, n - a line of plot on logarithmic paper, where the coordinates are scar diameter in millimetres and applied load in kilograms-force (or newtons), obtained under static conditions.
Hertz scar diameter, n - the average diameter, in millimetres, of an indentation caused by the deformation of the balls under static load (prior to test). It may be calculated from the equation
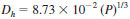
where:
Dh = Hertz diameter of the contact area, and
P = the static applied load.
homogeneity - the uniformity of the characteristics of the packaged material across the entire packaging run determined for the purpose of demonstrating the suitability of the batch for its intended purpose.
DISCUSSION - There are two homogeneity testing cases; one in which the material is ampulized as a reference material at the time of ampulization, and one in which the material is not.
(1) reference material at time of ampulization - The material to be ampulized is a reference material that has accepted true or consensus values. Ampulization of a reference material would require homogeneity testing in order to assess the variability caused by the ampulization process on the true or consensus values for the reference material.
(2) not a reference material at time of ampulization - The material to be ampulized is not a reference material at the time of ampulization but is intended to have characterization and assignment of true or consensus values at some future date. Rigid homogeneity testing is not required on such a material at the time of ampulization since the true or consensus values have not yet been determined. However, ampules must be retained at the beginning, middle, and end of the ampulization process. It is recommended that qualitative testing be done on at least one sample from each of the beginning, middle, and end of the ampulization process. The remaining ampules should then be retained for future homogeneity testing to determine quantitative or consensus values.
homogeneity, n - the ability of a test oil itself to remain the same in appearance throughout (uniform) after submission to a series of temperature changes.
hot-flame reaction, n - a rapid, self-sustaining, luminous, sometimes audible, reaction of the sample or its decomposition products with the atmosphere.
hot sticking, n - of piston rings, a condition in which the ring is stuck in its groove while the engine is running, normally indicated by varnish or other deposits on the outer face of the ring, by signs of blowby on the piston skirt, or both.
hot-stuck piston ring, n - in internal combustion engines, a piston ring that is stuck when the piston and ring are at room temperature, and inspection shows that it was stuck during engine operation.
DISCUSSION - The portion of the ring that is stuck cannot be moved with moderate finger pressure. A hot-stuck piston ring is characterized by varnish or carbon across some portion of its face, indicating that portion of the ring was not contacting the cylinder wall during engine operation.
hot tack, n - the cohesive strength during the cooling stage before solidification of a heat seal bond formed by a wax-polymer blend.
house fuel, n - for engine operation, a fuel that does not contain metallic additives used for engine warm-up and all non-octane rating engine operation.
house fuel, n - for octane rating, an unleaded, straight hydrocarbon fuel used for engine warm-up and all non-octane rating testing.
HPC, n - heterotrophic plate count
hydraulic fluid, n - liquid used in hydraulic systems for transmitting power.
hydraulic fluid, n - a liquid used in hydraulic systems for lubrication and transmission of power.
hydrolytic stability, n - the resistance of a material to permanent changes in properties due to reaction with water.

