lag phase, n - the period of diminished physiological activity and cell division following the addition of microorganisms to a new culture medium.
lamination, n - line of demarcation or elongated void generally parallel to the principal grain direction of a carbon or graphite body.
last nonseizure load, n - the last load at which the measured scar diameter is not more than 5 % greater than the compensation value at that load.
DISCUSSION - Shown in Fig. 1 as Point B.
lethal load XX (LLXX), n - a statistically or graphically estimated loading rate of test material that is expected to be lethal to XX % of a group of organisms under specified conditions for a specified time.
DISCUSSION - This terminology should be used for hydraulic fluids instead of the standard lethal concentration (LCXX) when the hydraulic fluid is not completely soluble under test conditions.
lethal load XX (LLXX), n - a statistically or graphically estimated loading rate of test material that is expected to be lethal to XX % of a representative subpopulation of organisms under specified conditions.
DISCUSSION - This terminology should be used instead of the standard LCXX when the material is not completely soluble at the test treat rates.
lethal load XX (LLXX), n - a statistically or graphically estimated loading rate of test material that is expected to be lethal to XX % of a subpopulation of organisms under specified conditions.
DISCUSSION - This terminology should be used for lubricants instead of the standard LCXX to designate that the material is not completely soluble at the test treat rates.
light distillate, n - in the petroleum industry, a distillate whose entire boiling range is below about 250°C (about 480°F).
DISCUSSION - Light distillates, such as naphtha or gasoline-range components, will have flash points at or below about 35°C (about 95°F), and thus can present greater hazards during storage and handling than materials with higher flash points, such as middle and heavy distillates.
DISCUSSION - Light distillate shall not be used to mean light middle distillate. (See middle distillate.)
light-duty, adj - in internal combustion engine operation, characterized by average speeds, power output, and internal temperatures that are generally much lower than the potential maximums.
light-duty engine, n - in internal combustion engine types, one that is designed to be normally operated at substantially less than its peak output.
DISCUSSION - This type of engine is typically installed in automobiles and small trucks, vans, and buses.
linear thermal expansion - the change in length per unit length resulting from a temperature change. Linear thermal expansion is symbolically represented by ΔL/L0, where ΔL is the length change of the specimen (L1 - L0), L0 and L1 are the specimens lengths at reference temperature T0 and test temperature T1, respectively. Linear thermal expansion is often expressed as a percentage or in parts per million (such as µm/m).
linearly mixable, adj - a property is deemed to be linearly mixable in a mass or volume measurement unit if the property of the mixed material can be calculated from the quantities and properties of the materials used to produce the mixture.
DISCUSSION - The general equations describing this linearly mixable attribute are as follows:
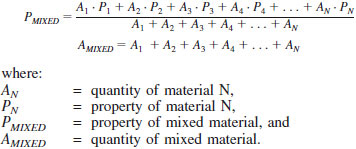
DISCUSSION - The material being mixed can be from the same process stream over time.
liquefied petroleum gases (LPG), n - narrow boiling range hydrocarbon mixtures, consisting mainly of propane or propylene, or both (Warning - Extremely flammable. Harmful if inhaled), butanes and butylenes, or both; in which the concentration of hydrocarbon compounds with boiling point greater than 0°C is less than 5 % by liquid volume, and whose vapor pressure at 37.8°C (100°F) is not greater than 1550 kPa.
liquid, adj - describing a state of matter that shows free flow and has a definite volume and indefinite shape, as determined by its container.
DISCUSSION - Sometimes a liquid is called a fluid, as in hydraulic fluid, a liquid.
DISCUSSION - A quantity of solid particles, powders, or pellets, for example, fluidized catalyst beds, can also flow like a liquid in the presence of an applied force. The state of the individual particles, nevertheless, remains as a solid.
liquid, n - substance (matter) in a liquid state (see liquid, adj).
load-carrying capacity, n - of a lubricating grease, the maximum load or pressure that can be sustained by a lubricating grease without failure of the sliding contact surfaces as evidenced by seizure or welding.
load-wear index (or the load-carrying property of a lubricant), n - an index of the ability of a lubricant to minimize wear at applied loads. Under the conditions of this test, specific loadings in kilograms-force (or newtons) having intervals of approximately 0.1 logarithmic units, are applied to the three stationary balls for ten runs prior to welding. The load-wear index is the average of the sum of the corrected loads determined for the ten applied loads immediately preceding the weld pair.
load-wear index, n - an index of the ability of a lubricant to prevent wear at applied loads. (Synonym - load-carrying property of a lubricant.)
loading rate, n - the ratio of test material to aqueous medium used in the preparation of a water accommodated fraction (WAF) and in interpretation of the results of a toxicity study with a poorly water soluble lubricant or lubricant component.
loading rate, n - the ratio of test material to aqueous medium used in the preparation of WAF, WSF, or mechanical dispersion and in the interpretation of the results of a toxicity study with a poorly water-soluble lubricant or lubricant component.
log phase, n - the period of growth of microorganisms during which cells divide at a positive constant rate.
longitudinal sonic pulse, n - a sonic pulse in which the displacements are in the direction of propagation of the pulse.
long-term storage, n - storage of fuel for longer than 12 months after it is received by the user.
lot, n - a definite quantity of a product or material accumulated under conditions that are considered uniform for sampling purposes.
lot - a quantity of calcined petroleum coke to be represented by a gross sample.
low resolution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, n - a form of NMR spectroscopy using a simple NMR analyzer that employs a low magnetic field and consequentially low NMR frequency. An example is proton NMR below 60 MHz. Resolution is expressed as time at half height of signal and is typically 1 millisecond (ms) or less.
low-temperature torque, n - the torque in g•cm required to restrain the outer ring of a No. 6204 size open ball bearing lubricated with the test grease while the inner ring is rotated at 1 ± 0.05 r/min at the test temperature.
low-volume connector, n - a special union for connecting two lengths of tubing 1.6-mm inside diameter and smaller; sometimes referred to as a zero dead-volume union.
LPG - abbreviation for liquefied petroleum gas.
LTMS, n - Lubricant Test Monitoring System
DISCUSSION - An analytical system in which ASTM calibration test data are used to manage lubricant engine test precision.
lubricant, n - any material interposed between two surfaces that reduces the friction or wear between them.
lubricant, n - any material interposed between two surfaces that reduces the friction or wear, or both, between them.
lubricant, n - any material interposed between two surfaces that reduces friction or wear between them.
DISCUSSION - In this test method, the lubricant is an oil which may or may not contain additives such as foam inhibitors.
lubricant, n - in manual transmission and final drive axles, lubricating oil.
lubricant base stock, n - a liquid that may be used alone as a lubricant, but normally is used as a major ingredient in formulated lubricants.
lubricant test monitoring system (LTMS), n - an analytical system in which ASTM calibration test data are used to manage lubricant test precision and severity (bias).
LTMS date, n - the date the test was completed unless a different date is assigned by the TMC.
LTMS time, n - the time the test was completed unless a different time is assigned by the TMC.
lubricating grease, n - a semi-fluid to solid product of a thickener in a liquid lubricant.
DISCUSSION - The dispersion of the thickener forms a two-phase system and immobilizes the liquid lubricant by surface tension and other physical forces. Other ingredients are commonly included to impart special properties.
lubricating grease, n - a semi-fluid to solid product of a dispersion of a thickener in a liquid lubricant.
DISCUSSION - The qualifying term, lubricating, should always be used. The term, grease, used without the qualifier refers to a different product, namely certain natural or processed animal fats, such as tallow, lard, and so forth.
DISCUSSION - The dispersion of the thickener forms a two-phase system and immobilizes the liquid lubricant by surface tension and other physical forces. Other ingredients are commonly included to impart special properties.
lubricating oil, n - a liquid lubricant, usually comprising several ingredients, including a major portion of base oil and minor portions of various additives.
lubricity, n - a qualitative term describing the ability of a lubricant to minimize friction between and damage to surfaces in relative motion under load.
lugging, adj - in internal combustion engine operation, characterized by a combined mode of relatively low-speed and high-power output.
luminometer number, n - a measure of the flame temperature in a wick lamp burning the candidate material as fuel at a specified flame radiation level in the green-yellow band of the visible spectrum.

